Animals Nervous System
Animals Nervous System: Overview
The nervous system of animals includes the brain and spinal cord. It helps control and coordinate all the body functions. The responses produced by the nervous system can be voluntary or involuntary.
Important Questions on Animals Nervous System
Assertion: Corpus callosum is present in space between the dura mater and pia mater.
Reason: It serves to maintain the constant intracranial pressure.
Identify the correct functions of a nerve cell.
Draw the diagram showing structure of human brain. Label the following parts.
i) Cerebrum ii) Cerebellum
The neuromuscular junction is made up of the dendrite of a motor neuron and a muscle fibre.
Free nerve endings are most abundant in
What is free nerve ending? What is its function in the skin?
In neurons, nucleus is located in the cell body.
Explain the function of nervous tissue.
Fill in the blank with the correct answer given in the bracket.
Nervous tissue sends the motor nerve impulses to _____ for action. (brain, spinal cord, muscles)
Nervous tissue cannot give a response.
The number of receptors does not influence the efficiency of sense organs.
The number of receptors in the sense organs is the same in different organisms.
What are the main functions of the spinal cord?
Motor neurons conduct impulses from sensory organs to the brain and the spinal cord.
The motor nerves deliver the stimuli
Throwing ball and writing are involuntary actions.
The correct path of movement of nerve impulses in the following diagram is
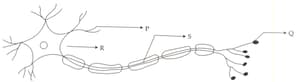
The longest branch arising from the cyton of a neuron is called
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Dendron | a. Controlled by the medulla oblongata |
| 2. Vertebral column | b. Carry impulses to effector organs |
| 3. Impulses | c. Irregular folds on outer surface |
| 4. Effector organs | d. Nerve |
| 5. Bundles of axons | e. Fatty white substance covering an axon |
| 6. Swallowing | f. Distributes nutrients to the brain |
| 7. Motor nerves | g. Glands and muscles |
| 8. Myelin sheath | h. Has many branches |
| 9. Cerebrum | i.Messages encoded as electrical signals |
| 10. Cerebrospinal fluid | j. Protects the spinal cord. |
